» What is fog computing?
» How does fog computing work?
» What are the benefits of fog computing?
» How does fogging work in an IoT environment?
» What are the key applications of fog computing?
» How to get started with fog computing?
» Fogging with Ignition
» Explore Ignition
Other knowledge base articles
» IIoT
» Edge Computing
» Industry 4.0
» Industrial Automation
» MQTT
» […]

Fog Computing
What is fog computing?
It resembles edge computing, but the technology employs small computers or servers that are closer to the edge of the network instead of processing data on devices located very close to the data source, such as sensors in a factory.
Think of it like a foggy morning, where the fog represents the data coming from the source (like a sensor), and the fog computing infrastructure is the mist hovering just above the ground. This infrastructure absorbs and processes the mist instead of letting it travel all the way to the clear sky (the cloud).
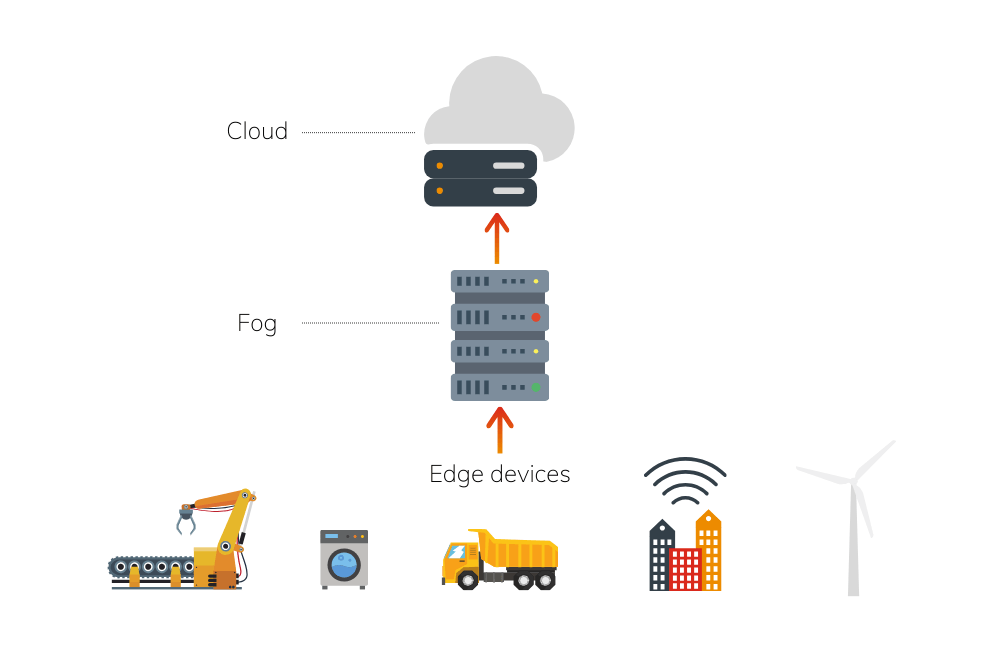
This technology processes data faster and more efficiently than if it were all sent to the cloud. This is useful for applications like smart cities, where sensors throughout the city collect data and need to process it quickly, for example, to manage traffic. It combines the benefits of edge computing with the scalability of cloud computing to provide the best solution for processing data in the right place and at the right time.
How does fog computing work?
This technology can be implemented in various ways depending on the specific application. Some implementations use physical fog nodes located at different locations, while others use virtual fog nodes hosted in the cloud. In general, fogging works through the following steps:
- Devices and sensors collect data and send it to a nearby fog node.
- The fog node processes the data locally using its own computing resources, reducing network load and lowering latency.
- After the data is processed, the fog node sends it to a nearby cloud server or another endpoint for further processing or storage.
- Based on the processed data, decisions can be made and actions taken, such as adjusting the operation of a machine or triggering an alarm.
It can also be combined with other technologies, such as machine learning and artificial intelligence, to gain new insights and make better decisions based on the collected data.
What are the benefits of fog computing?
It offers several advantages over traditional cloud computing or other distributed computing architectures:
- Faster data processing: It brings computing resources closer to the devices, resulting in faster data processing. This leads to lower latency and faster decision-making.
- Reduction of network load: The amount of data that needs to traverse the network decreases. This is particularly important for applications where bandwidth is limited or costly.
- Improved security and privacy: Data processing and storage occur locally, reducing the risk of data loss or hacking. This also alleviates concerns about data privacy, as the data does not travel to external servers.
- Scalability: Fog computing offers scalability on a smaller scale than cloud computing. This means it’s easier to add or remove computing resources based on application needs.
- Cost savings: The costs of bandwidth and network usage are lower, while retaining the benefits of faster data processing and better performance.
- Better reliability and availability: Applications continue to function even if the connection to the cloud server is disrupted.
- Enhanced user experience: Faster data processing and lower latency result in better performance and user experience. This leads to higher customer satisfaction and improved business outcomes.
How does fogging work in an IoT environment?
Fog computing plays a crucial role in the IoT (Internet of Things) ecosystem. The IoT comprises a network of physical objects equipped with sensors, software, and connectivity to collect and exchange data with other devices and systems.
It provides benefits to the IoT by enabling data processing closer to the source, rather than sending it to the cloud for processing. This results in lower latency, improved network bandwidth, and greater efficiency in data processing. Additionally, fog computing helps to enhance data security by processing data locally, thereby enhancing privacy and security.
Fog computing can be applied in various IoT applications, such as smart cities, smart buildings, smart energy grids, smart transportation and logistics, and more. For example, in smart cities, fog computing can be utilized to collect data from sensors installed in streetlights, traffic lights, and other public infrastructure. This data can then be processed locally to provide real-time traffic management, leading to more efficient traffic control and reduced congestion.
What are the key applications of fog computing?
It enhances efficiency and productivity in factories and manufacturing environments by collecting data from sensors and machines. This enables real-time decision-making about production processes and scheduling maintenance and repairs before issues arise.
Sensors installed in public infrastructure such as streetlights, traffic lights, and parking garages collect and process data in smart cities. Fog computing assists in optimizing traffic flows, saving energy, and improving pedestrian and cyclist safety.
The healthcare sector improves efficiency and enhances the quality of care through the use of fog computing. This involves remote patient monitoring, collecting and analyzing data from medical devices, and improving access to medical information.
By collecting and processing data from sensors installed in energy infrastructure, such as smart meters and solar energy installations, smart energy networks can be optimized. This helps improve energy generation efficiency, reduce CO2 emissions, and optimize energy consumption.
The transportation and logistics sector utilizes fog computing by collecting and processing data from sensors installed in vehicles, containers, and warehouses. This allows the sector to optimize transportation routes, improve the efficiency of logistics processes, and reduce costs.
How to get started with fog computing?
If you want to get started with fog computing, here are some steps to follow:
- Make sure you understand what fog computing is and how it differs from other computing architectures such as cloud computing and edge computing.
- Identify what you want to use fog computing for.
- Choose the right hardware suitable for fog computing. This ranges from small single-board computers to advanced industrial gateways, depending on the application.
- Select the appropriate software needed to process the data and run the applications. This varies from operating systems to specific fog computing platforms and tools.
- Deploy the hardware and software and test the system to ensure it meets the requirements and delivers the desired performance.
- If the system is working properly, you can scale it to process more data or support more users.
- Make sure to regularly maintain and monitor the system to ensure it continues to work as intended and to quickly address any issues.
It’s also important to remember that fog computing is a complex technology, and it may be beneficial to collaborate with experts in this field to ensure you achieve the best possible results.
Fogging with Ignition
The difference between fog computing in Ignition and other packages mainly lies in architecture and functionality. Firstly, Ignition offers an integrated development environment and a platform for building and deploying fog computing solutions. This makes it easier for developers to build their applications and integrate them with various hardware and software components.
Additionally, Ignition provides powerful functionality for data acquisition, analysis, and visualization. This enables users to collect real-time data from various sources, analyze this data, and create insightful dashboards for users at different levels in the organization.
Another key difference is that Ignition is an open platform, meaning it can integrate with a wide range of hardware and software components from different vendors. This makes it easier to integrate existing systems and equipment into a fog computing solution.
Lastly, Ignition also offers extensive capabilities for security and access control, ensuring that users have secure access to the data and systems they need.
In summary, the combination of an integrated development environment, powerful functionality, openness, and security make fog computing in Ignition a powerful and unique solution.
Discover Ignition
your way
Start building
For developers
Get started with your own Ignition applications right away.
- Download and install Ignition easily and quickly.
- Explore all features.
- Connect unlimited tags, PLCs, databases, and devices.
Discover how Ignition solves your technical challenges without limitations.
See Ignition in action
For managers
Explore Ignition without any technical knowledge in the demo environment.
- No installation required.
- See how Ignition automates and visualizes processes.
- Adjust live values and see instant results.
Experience real-time automation and discover what it can offer your business.
Want to really know what Ignition can do for you?
Let us come to you for a free demo.
- Meet with our experts and ask all your questions.
- Get personalized advice.
- See how Ignition can optimize your processes.
The perfect opportunity to collaborate with specialists and see exactly how Ignition can help you achieve your business goals.
Start building your own application now!

Discover how Ignition can improve your processes!
Want to see how Ignition automates and visualizes processes without any technical knowledge? Fill out the form and gain immediate access to the demo environment, where you can experience Ignition live.

Schedule a no-obligation demo with our experts!
Want to learn more about how Ignition can optimize your processes? Request a personalized demo and discuss your business goals with our specialists. Fill out the form to book an appointment.

