» What is an HMI?
» How does an HMI work?
» What is a High Performance HMI?
» Who uses HMI?
» The benefits of an HMI
» Examples
» HMI and PLC
» What is the difference between HMI and SCADA?
» Trends in HMI technology
» What software is available?
» HMI and Ignition
» Explore Ignition
Other knowledge base articles

HMI
» What is an HMI?
» How does an HMI work?
» What is a High Performance HMI?
» Who uses HMI?
» The benefits of an HMI
» Examples
» HMI and PLC
» What is the difference between HMI and SCADA?
» Trends in HMI technology
» What software is available?
» HMI and Ignition
» Explore Ignition
What is an HMI?
HMI stands for Human Machine Interface, also known as MMI (Man Machine Interface). This is a user interface or dashboard that connects a person to a machine, system, or device. It can consist of various components such as a screen, keyboard, mouse, touchpad, or joystick.
It provides a user interface through which a human can interact with a machine and perform various tasks, such as setting parameters, monitoring machine performance, and viewing data.
Just as you can control and regulate the temperature in your home with your air conditioning system, an operator on the factory floor can use an HMI to control and regulate the temperature of an industrial water tank or to see if a particular pump in the factory is currently running.
The goal is to make it easier for humans to work with the machine and to improve productivity. Previously, operators had to constantly walk around the production floor to view mechanical progress and record it on a piece of paper or a whiteboard. By enabling PLCs to send real-time information directly to an HMI display, this outdated practice is eliminated, preventing many costly problems due to lack of information or human error.
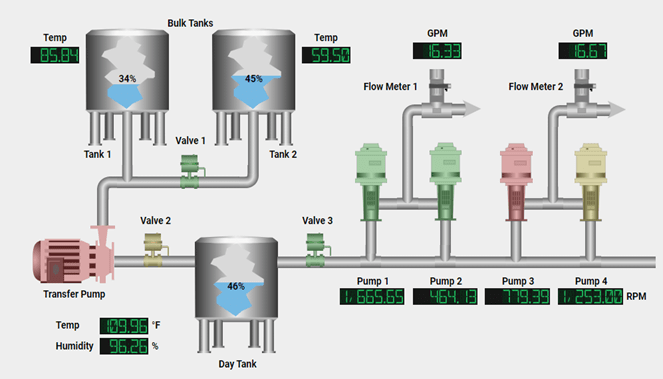
How does an HMI work?
An HMI works by providing an interface between a human and a machine. This typically involves a graphical screen, a keyboard, and a mouse or touchpad through which the user operates the machine and receives information about the machine’s performance.
These systems are designed to gather information from machines (via PLC’s), analyze it, and then present it to the user in a visually appealing manner. The system also provides various functions for monitoring and controlling the machine, such as setting parameters, starting and stopping the machine, and handling alarms.
Modern HMIs often use touchscreen technology and intuitive user interfaces to simplify the interaction between the user and the machine. This includes the use of icons, buttons, and sliders to facilitate machine operation. A well-designed interface enables the user to operate the machine more efficiently and prevents errors that may occur due to unclear or confusing control interfaces.
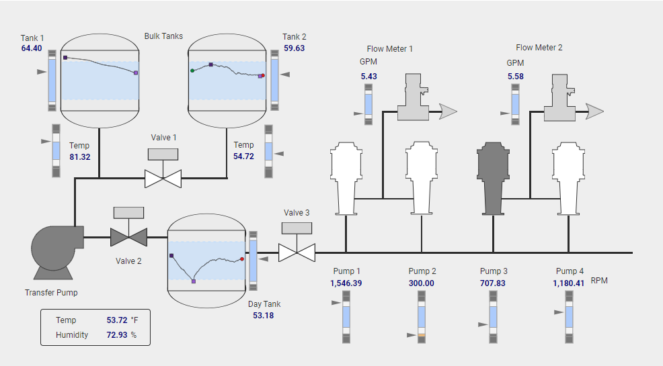
What is a High Performance HMI?
A High Performance HMI is an enhancement of the standard version and is designed to improve user efficiency and effectiveness. High Performance HMIs are created with the goal of reducing errors and enhancing operator decision-making, thereby making production more efficient and effective. This is achieved through the use of more intuitive and visually appealing interfaces that present key information better and clearer to the user.
Some features include:
- Color usage: Colors are tailored to the environment and user, making important information stand out immediately and easier to find.
- Graphs and trends: Better data visualization allows users to recognize patterns faster and identify key information.
- Advanced alarm and alert systems: This immediately notifies users of issues and malfunctions, enabling them to intervene quickly to resolve problems.
- Intuitive navigation and layout: Users can quickly and easily find the information they need.
- Contextual information: They provide contextual information to help the user understand the information and make decisions.
- Ergonomics: They are designed with ergonomics in mind, allowing users to work comfortably and safely.
Who uses HMI?
This technology is used in almost all industrial organizations for interaction with their machines and optimizing their industrial processes. Below are some examples of who uses them in those organizations and why:
- Operators, the individuals who operate and monitor the machines, are the primary users. The interface provides them with real-time information about the status of the machines and enables them to operate the machines more efficiently and effectively.
- Technicians primarily use them for diagnosis and troubleshooting. They use the interface to identify the cause of a malfunction and quickly get the machine back up and running.
- Engineers use them for designing and optimizing machines and production lines. The collected data is used to analyze and improve machine performance.
- Managers use them to monitor and optimize production processes. They use the collected data to increase productivity, reduce costs, and improve the efficiency of production processes.
The benefits of an HMI
- Improved operation: They make it easier for users to operate machines through intuitive interfaces that utilize touchscreen technologies and easily understandable icons and buttons.
- Monitoring and diagnosis: They provide real-time monitoring and diagnosis of machines, alerting users immediately to problems and malfunctions and enabling quick problem resolution.
- Safety: They are designed with user and machine safety in mind. They provide features such as emergency stop buttons and warning signals to create a safe working environment for operators.
- Efficiency: They increase production efficiency by reducing machine downtime, optimizing production capacity, and lowering costs.
- Data collection: They collect data on machine performance and present this information to the user. This helps identify trends and make decisions about optimizing production.
- Flexibility: They are flexible and customizable to the specific needs of a machine or production line.
Examples
Industrial control panels
These are the most common examples of HMIs. These panels are used for the local operation and monitoring of machines and processes in the factory environment.
Touchscreens
Touchscreens are used in a wide range of applications, such as smartphones, tablets, ATMs, etc. They provide an intuitive way to control devices and display data.
Remote control systems
Remote control systems use this technology to operate and monitor devices and machines remotely. They are often used in applications such as home automation, oil and gas field monitoring, etc.
Digital displays
Digital displays are used to show information such as temperature, pressure, speed, etc. They can be found on various devices, from coffee makers to airplanes.
Dashboard software
Dashboard software utilizes this technology to visualize and analyze business data. They are used in applications such as business intelligence, performance monitoring, etc.
HMI-based robots
These robots use HMI technology to communicate with their human operators. They are used in applications such as production lines, warehouses, etc.
HMI and PLC
HMI and PLC are two different but closely related technologies that are often used together in industrial automation. A PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) is an electronic device used to automatically control machines and processes. It receives data from sensors and other input devices and then executes programmable tasks to control the outputs of the machine or process.
They often work together as part of an automated system. The PLC performs the programmable tasks to control the machine or process, while the HMI is used to display the status of the machine or process and enable interaction with the system. The HMI can also alert the operator if there are any issues, such as errors or malfunctions in the machine or process.
In general, it can be said that the PLC is responsible for automating the process, while the HMI provides the interface for human interaction with the process.
What is the difference between HMI and SCADA?
Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) and HMI are closely related and are often mentioned in the same context because they both are part of a larger industrial control system, but they each offer different functionalities and capabilities.
While HMIs focus on visually conveying information to assist the user in monitoring an industrial process, SCADA systems have a greater capacity for data collection and control of the control system.
Unlike SCADA systems, HMIs do not collect and log information or connect to databases. Instead, the HMI is more of an effective communication tool that operates as part of or alongside a SCADA system.
Trends in HMI technology
Increasing use of touchscreen
In recent years, there has been a strong shift towards the use of touchscreen interfaces in HMIs. This is because touchscreens provide an intuitive way to operate and monitor machines and processes.
Use of mobile devices
HMI technology is now available on mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets, allowing operators to view real-time data and control processes even when they are not at the workplace.
Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
By integrating AI technology into HMIs, machines and processes become smarter and can operate more autonomously, improving efficiency and reducing operational costs.
Enhanced visualization
HMIs now use advanced visualization technologies, such as 3D modeling, to represent machines and processes realistically, providing operators with a better understanding of how machines and processes operate.
Cloud-based HMI
HMI technology is now delivered via cloud-based platforms, allowing operators worldwide to access and control machines and processes from anywhere and monitor them.
Use of Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
By integrating VR and AR technologies into HMIs, operators can virtually step into a machine or process and view it up close, improving operational efficiency and reducing maintenance costs.even, waardoor operators een beter begrip krijgen van de werking van machines en processen.
What software is available
There are many different HMI software packages available for various applications and industries. Below are some examples of popular HMI software:
- FactoryTalk View by Rockwell Automation: FactoryTalk View is popular HMI software for the automation industry. It offers a range of features for creating HMI applications, including animated graphic objects, alarm management, and advanced trending.
- Wonderware InTouch by Schneider Electric: Wonderware InTouch is HMI software used in industrial processes. It provides features such as alarm management, reporting, trending, and integration with external databases.
- Ignition by Inductive Automation: Ignition is HMI software focused on flexibility and ease of use. It offers a range of features for creating HMI applications, including animated graphic objects, alarm management, reporting, and advanced scripting capabilities.
- WinCC by Siemens: WinCC is HMI software used in industrial automation. It offers a range of features for creating HMI applications, including animated graphic objects, alarm management, reporting, and integration with external databases.
- VTScada by Trihedral: VTScada is HMI software focused on ease of use and flexibility. It offers a range of features for creating HMI applications, including animated graphic objects, alarm management, reporting, and integration with external databases.
- IntegraXor by Ecava: IntegraXor is HMI software focused on ease of use and cost savings. It offers a range of features for creating HMI applications, including animated graphic objects, alarm management, and reporting.
These are just some examples of popular HMI software. There are many more HMI software packages available on the market, each with their own unique set of features and capabilities.
HMI and Ignition
These are closely related technologies that are often used together in industrial automation. Ignition is HMI software focused on flexibility and ease of use. It offers a range of features for creating HMI applications, including animated graphic objects, alarm management, reporting, and advanced scripting capabilities. Ignition is often used in industrial processes to collect, analyze, and visualize data and to enable operators to monitor and manage machines and processes.
By integrating these technologies, operators are able to collect, analyze, and gain insights into the performance of machines and processes. This improves production efficiency, reduces costs, and enhances safety.
What are the advantages of Ignition compared to other HMI software?
- Flexibility: Ignition is highly flexible and easily adaptable for use in various applications and industries. It can be integrated with different databases, protocols, and devices.
- Ease of use: Ignition is designed with ease of use in mind. It has an intuitive user interface and utilizes drag-and-drop functionality to design HMI screens.
- Scalability: Ignition is scalable and can be used for both small and large systems. It can also be used across multiple locations and integrated with different databases and other systems.
- Security: Ignition has built-in security features that restrict access to the HMI to authorized users. It also provides capabilities for managing alarms and alerts to improve safety.
- Cost savings: Ignition is cost-effective compared to other HMI software packages. It offers a free trial version and an unlimited free development license, allowing users to try out the system before investing in a license.
- Advanced features: Ignition offers advanced features such as advanced scripting, animated graphic objects, powerful trend analysis, and reporting capabilities.
All these distinctive advantages make Ignition a popular choice for industrial automation systems.
Discover Ignition
your way
Start building
For developers
Get started with your own Ignition applications right away.
- Download and install Ignition easily and quickly.
- Explore all features.
- Connect unlimited tags, PLCs, databases, and devices.
Discover how Ignition solves your technical challenges without limitations.
See Ignition in action
For managers
Explore Ignition without any technical knowledge in the demo environment.
- No installation required.
- See how Ignition automates and visualizes processes.
- Adjust live values and see instant results.
Experience real-time automation and discover what it can offer your business.
Want to really know what Ignition can do for you?
Let us come to you for a free demo.
- Meet with our experts and ask all your questions.
- Get personalized advice.
- See how Ignition can optimize your processes.
The perfect opportunity to collaborate with specialists and see exactly how Ignition can help you achieve your business goals.
Start building your own application now!

Discover how Ignition can improve your processes!
Want to see how Ignition automates and visualizes processes without any technical knowledge? Fill out the form and gain immediate access to the demo environment, where you can experience Ignition live.

Schedule a no-obligation demo with our experts!
Want to learn more about how Ignition can optimize your processes? Request a personalized demo and discuss your business goals with our specialists. Fill out the form to book an appointment.

