» What is industry 4.0?
» The industrial revolutions in chronological order
» Which sectors can benefit from industry 4.0?
» What are the advantages of industry 4.0?
» What are the key technologies behind industry 4.0?
» When does your factory become a smart factory?
» What challenges arise with industry 4.0?
» How do you prepare your company for industry 4.0?
» Industry 4.0 and Ignition
» Explore Ignition
Other knowledge base articles
» AI
» Edge Computing
» MQTT
» IIoT
» Industriële Automatisering
» […]

Industry 4.0
» What is industry 4.0?
» The industrial revolutions in chronological order
» Which sectors can benefit from industry 4.0?
» What are the advantages of industry 4.0?
» What are the key technologies behind industry 4.0?
» When does your factory become a smart factory?
» What challenges arise with industry 4.0?
» How do you prepare your company for industry 4.0?
» Industry 4.0 and Ignition
» Explore Ignition
What is industry 4.0?
Industry 4.0 refers to the fourth industrial revolution, where production systems and factories are connected with advanced technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), cloud computing, and big data. The goal of Industry 4.0 is to increase productivity and efficiency, improve quality, and reduce costs. By leveraging advanced technologies, production processes can be optimized and automated, leading to a more flexible and responsive manufacturing environment. Industry 4.0 has potential for numerous sectors, including manufacturing, healthcare, transportation, logistics, energy, agriculture, and many others.
The industrial revolutions in chronological order
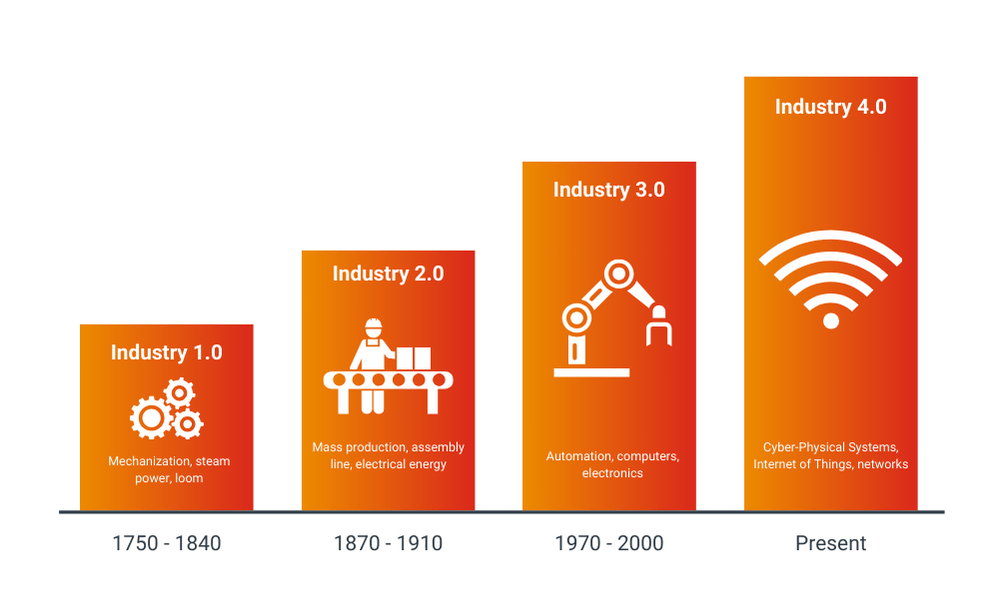
The four industrial revolutions have each brought about changes in the way businesses produce and manufacture goods.
First industrial revolution
The first industrial revolution took place in the late eighteenth and early nineteenth centuries. The rise of the steam engine and the mechanization of the textile industry characterize this revolution. The use of water and steam power made it possible to use machines on a large scale for the production of goods. This led to large-scale production and an increase in labor productivity.
Second industrial revolution
The second industrial revolution took place at the end of the nineteenth and beginning of the twentieth centuries. Characteristic of this revolution is the emergence of electricity, mass production, and the assembly line. The introduction of the assembly line made it possible to streamline and accelerate production processes. This resulted in a significant increase in productivity.
Third industrial revolution
The third industrial revolution, also known as the digital revolution, took place in the late seventies and eighties of the twentieth century. Characteristic of this revolution is the rise of computers and IT technologies. The introduction of automated systems and robotics made it possible to further automate and accelerate production processes. This led to an even greater increase in productivity.
Fourth industrial revolution
The fourth industrial revolution, also known as Industry 4.0, began in the early twenty-first century. The rise of advanced technologies such as the IoT, AI, cloud computing, and big data characterize this revolution. These technologies make it possible to further optimize, automate, and digitize production processes. This creates a more flexible and responsive production environment that is better adapted to the demands of the modern economy.
Which sectors can benefit from industry 4.0?
Industry 4.0 has the potential to impact various sectors, including:
- Manufacturing: Optimizing production processes and improving communication and collaboration between different machines increases productivity.
- Logistics and supply chain management: Tracking goods in real-time, reducing inventory surpluses, and lowering costs improves the efficiency of logistics processes.
- Healthcare: Improving healthcare quality through the use of IoT devices, robots, and AI technologies. This leads to more efficient and effective care.
- Agriculture: It helps improve production process efficiency and reduce reliance on human labor. This includes the use of robots, drones, and other technologies.
- Energy: Improving the efficiency of renewable energy production, such as solar and wind energy. Also, reducing energy waste by monitoring and optimizing energy consumption.
- Transportation and mobility: Deploying smart vehicles, IoT devices, and AI technologies. This leads to better mobility and reduced traffic congestion.
Overall, every sector involved in the production and delivery of goods and services benefits from the advantages offered by Industry 4.0.
What are the advantages of industry 4.0?
- More efficient production: Streamlining and automating production processes improves efficiency and results in shorter production times.
- Higher quality: It is possible to conduct better quality control, resulting in fewer product defects. This improves the quality of the end product.
- More flexibility: Smart factories adapt quickly to changing market conditions and customer needs.
- Better inventory management: Companies are able to better manage their inventories and optimize inventory levels. This reduces costs and increases efficiency.
- Lower costs: Automation and efficiency lead to significant cost savings, resulting in higher profitability.
- Improved safety: Smart factories have better safety control and monitoring. This improves the safety of workers and product environments.
- More insight into production processes: Using real-time data analysis and monitoring, companies gain insights into production processes. This enables them to solve problems more quickly.
- Sustainability: Implementing energy-efficient and sustainable technologies reduces companies’ ecological footprint. This enhances their reputation as a sustainable enterprise.
What are the key technologies behind industry 4.0?
There are various technologies that form the foundation of Industry 4.0, such as:
Internet of Things (IoT)
Enables devices and machines to communicate with each other and collect and analyze data.
Big data analytics
Analyzes large amounts of data about production processes, employees, and customers to gain valuable insights.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Used to make automated decisions and optimize production processes. For example, AI can be used to perform predictive maintenance on machines to prevent production downtime.
Augmented Reality (AR)
Supports workers in performing important tasks by displaying key information to them in real time. It can also be used for employee training and creating virtual prototypes.
Additive manufacturing
Also known as 3D printing.
Cyberfysieke systemen (CPS)
These consist of interconnected machines, sensors, and computers used to manage and optimize production processes.
Cloud computing
A method of data storage and processing that allows businesses to easily access data and applications from any location.
Robots
Used to perform repetitive tasks and improve the efficiency of production processes.
These technologies work together to create an integrated and optimized production process, resulting in a more efficient and effective production.
When does your factory become a smart factory?
A factory becomes a smart factory when it is equipped with advanced technologies and systems that optimize, automate, and digitize production processes. A smart factory is connected with advanced technologies that link machines and devices together and gather data about the production process.
It utilizes automated systems and robots to streamline and accelerate production processes. Additionally, it also employs advanced analytics tools to collect and analyze real-time data. This enables quicker identification and resolution of issues.
A smart factory is designed to be flexible and adapt quickly to changing market conditions and customer needs. It leverages advanced technologies to improve energy efficiency and reduce the environmental impacts of production. It also employs collaborative systems that enable workers and machines to efficiently collaborate and optimize production processes.
What challenges arise with industry 4.0?
Just as with any major shift, there are challenges inherent in implementing Industry 4.0, such as:
- Security: Smart factories are connected to the internet and other networks, making them more susceptible to cyberattacks. Therefore, robust security measures are essential.
- Data privacy: Smart factories collect vast amounts of data about production processes, employees, and customers. This requires careful management of data privacy.
- Employee training: Implementing new technologies requires training employees to understand and work with them.
- System integration: Integrating existing systems with new technologies can be challenging and often requires customization.
- Interoperability: Smart factories utilize various technologies and systems that must seamlessly communicate with each other.
- Costs: Implementing new technologies and systems often involves high costs and a long return on investment period.
- Change management: Transitioning to a smart factory often requires a shift in organizational culture and may face resistance from employees unfamiliar with the new technologies and systems.
- Regulatory compliance: The rise of smart factories necessitates new regulations to protect data privacy and manage security risks.
Successfully addressing these challenges is crucial for companies looking to reap the benefits of Industry 4.0.
How do you prepare your company for industry 4.0?
If you want to prepare your company for Industry 4.0, here are some steps you can take:
- Ensure you have a good basic understanding of key technologies like IoT, big data, cloud computing, and AI, and how they can be applied in your business.
- Assess your existing IT infrastructure to determine if it’s sufficient to meet the demands of Industry 4.0.
- Consider whether you need to invest in new equipment or software to modernize your business.
- Provide your employees with the necessary education and training so they can work with the new technologies and processes required for Industry 4.0.
- Utilize data analytics to gain insights into your production processes and business performance. Use these insights to optimize processes and make them more efficient.
- Collaborate with other companies and industry experts in the field of industry 4.0 to discover and implement new technologies and ideas in your business.
- Ensure proper security measures are in place for your IT systems, as increased connectivity also brings a higher risk of cyberattacks.
By taking these steps, you’ll prepare your company for the challenges and opportunities that come with Industry 4.0. It’s important to stay up-to-date with the latest developments and continue innovating to gain and maintain a competitive advantage.
Industry 4.0 and Ignition
Ignition is a software platform for industrial automation that can be used for Industry 4.0 applications. Ignition provides solutions for data acquisition, process monitoring, visualization, and reporting, among other features. The platform leverages modern technologies such as MQTT, OPC-UA, and Python, allowing seamless integration with other Industry 4.0 solutions and systems.
For example, Ignition can be used to collect data from machines and processes in a production environment and analyze it using machine learning techniques. This improves production efficiency and enables process optimizations. Ignition can also generate real-time dashboards and reports, providing operators and managers with quick insights into the status of the production environment and potential areas for improvement.
In short, Ignition is a software platform that aligns with Industry 4.0 technologies and contributes to enhancing the efficiency and performance of production processes.
Why is Ignition the ultimate platform for industry 4.0?
- Scalability: It can easily scale from small applications to large, complex systems, accommodating businesses of various sizes and growing alongside their needs.
- Customization: Ignition can be tailored to fit the specific needs of a business, offering flexibility in configuration, integration with other systems, and customization of the user interface.
- Open standards: By utilizing open standards like OPC UA and MQTT, Ignition ensures seamless integration with other systems and devices, a crucial aspect for Industry 4.0 applications where interoperability is essential.
- Intuitive interface: With an intuitive interface that can be customized to users’ specific preferences, Ignition is easy to use for operators and other employees in the production environment.
- Advanced analytics: Ignition offers advanced analysis capabilities, including machine learning and predictive analytics, providing businesses with insights into their production processes to further optimize operations.
Discover Ignition
your way
Start building
For developers
Get started with your own Ignition applications right away.
- Download and install Ignition easily and quickly.
- Explore all features.
- Connect unlimited tags, PLCs, databases, and devices.
Discover how Ignition solves your technical challenges without limitations.
See Ignition in action
For managers
Explore Ignition without any technical knowledge in the demo environment.
- No installation required.
- See how Ignition automates and visualizes processes.
- Adjust live values and see instant results.
Experience real-time automation and discover what it can offer your business.
Want to really know what Ignition can do for you?
Let us come to you for a free demo.
- Meet with our experts and ask all your questions.
- Get personalized advice.
- See how Ignition can optimize your processes.
The perfect opportunity to collaborate with specialists and see exactly how Ignition can help you achieve your business goals.
Start building your own application now!

Discover how Ignition can improve your processes!
Want to see how Ignition automates and visualizes processes without any technical knowledge? Fill out the form and gain immediate access to the demo environment, where you can experience Ignition live.

Schedule a no-obligation demo with our experts!
Want to learn more about how Ignition can optimize your processes? Request a personalized demo and discuss your business goals with our specialists. Fill out the form to book an appointment.

