» What is OPC?
» Data Access
» Alarms & Events
» Historical Data Access
» Unified Architecture
» How does OPC work?
» What are the benefits?
» What role does this protocol play in industry 4.0?
» Who uses it?
» OPC and SCADA
» OPC and Ignition
» Explore Ignition
Other knowledge base articles

OPC
What is OPC?
OPC stands for Open Platform Communications. It is an industrial communication protocol for the transfer of data between various control systems and equipment in manufacturing and process industries.
It provides a standardized way to collect, analyze, and make data available from different control systems and equipment to business applications and systems. This enables companies to monitor, optimize, and automate production processes and to obtain decision-supporting information.
There are several versions available, each offering specific features and capabilities for communication between control systems and production equipment:
- Data Access
- Alarms & Events
- Historical Data Access
- Unified Architecture
Data Access
OPC DA is the oldest and simplest protocol. It sends data from control systems directly to other systems on the factory floor. With OPC DA, applications collect real-time data from various devices and systems, visualizing this data or using it to make decisions. It uses an efficient communication protocol to transfer data quickly and reliably between different applications. One of the limitations of OPC DA is that it can only collect and share real-time data. It does not support historical data or complex data structures.
Alarms & Events
OPC AE is an extension of the OPC protocol designed to collect and share information about alarms and events between various industrial automation systems. With OPC AE, users collect information about the status of devices and processes and receive alerts when deviations occur or when there are system failures. It also provides the ability to use advanced filters to collect only relevant information, improving system performance and reducing network load.
Historical Data Access
OPC HDA is an extension of the OPC protocol designed to collect and share historical data from industrial automation systems between different applications. It enables the use of collected historical data to analyze trends and patterns and to generate reports. This assists in identifying issues and making decisions about system improvements and optimizations. However, HDA is an older version and is less commonly used in industrial automation systems today.
Unified Architecture
OPC UA is the latest and most modern version. It offers several advantages over previous versions. For instance, it supports various operating systems, programming languages, and platforms. It also provides better security and authentication, including encryption, digital signing, and certificate management.
It is designed with a focus on interoperability and provides a standardized way of exchanging data between different systems and devices, regardless of the vendor or device type. This enables companies to more easily integrate different devices and systems and share data across various departments and organizations.
OPC UA is also designed to meet the requirements of Industry 4.0 and IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) environments, where a large number of devices and systems exchange data via the internet and cloud services. As a result, OPC UA has become a significant standard in industrial automation and is used in a wide range of applications.
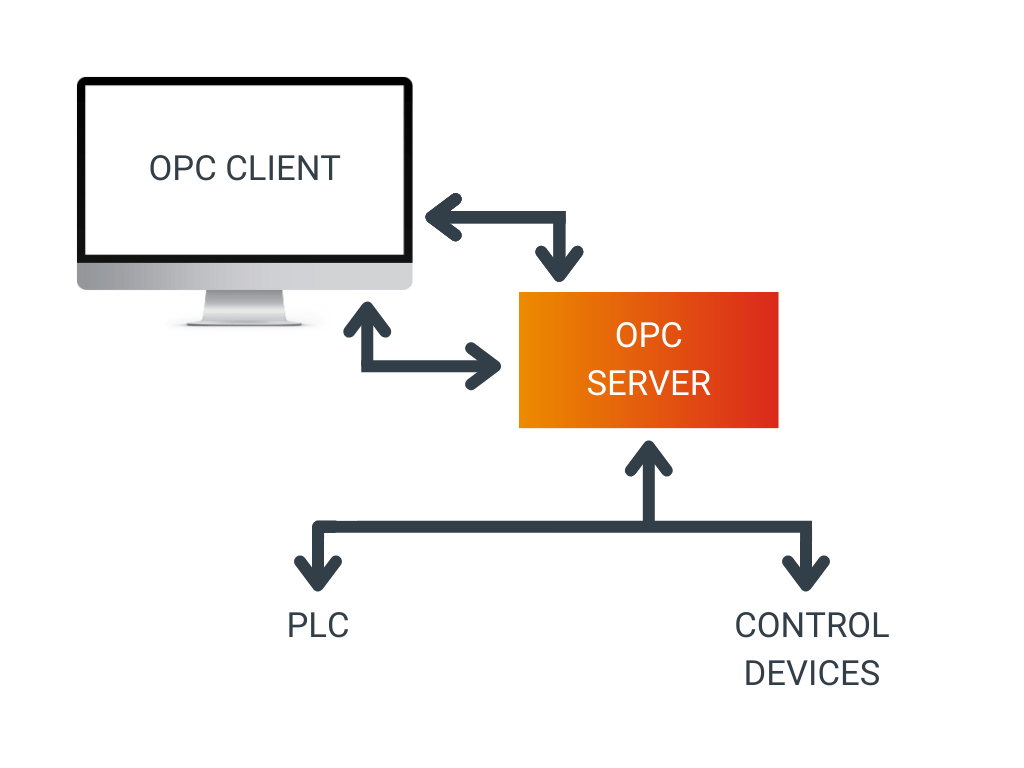
How does OPC work?
OPC functions through a client-server model. An OPC server is a software application that provides access to data from a specific device or process, such as a PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) or a SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) system. The OPC client is an operating system that accesses this data via the OPC server.
When a client connects to a server, a process is initiated to establish the connection and secure the data exchange. Subsequently, the client can request the available data from the server and update this data in real-time.
What are the benefits?
- Interoperability: It is a standardized way to exchange real-time data between different devices and systems from different vendors. This allows for seamless integration of various systems and data exchange without the need for special interfaces or custom code.
- Efficiency: It utilizes an efficient communication protocol to transfer data quickly and reliably between systems and devices. This reduces latency and increases the speed of data exchange, enabling faster responses to changes in the production environment.
- Reliability: It is designed to provide reliable data exchange, even in environments with high interference and disturbances. It offers various security and fault tolerance mechanisms to ensure that the exchanged data is accurate and consistent.
- Security: It employs encryption and digital certificates to ensure the security of data exchange. This reduces the risk of unauthorized access to data and protects businesses from potential cyber attacks.
- Scalability: It is scalable and can be used in both large and small production environments. It allows for easy connection of new devices and systems to the network without requiring major changes to the software.
What role does this protocol play in industry 4.0?
This protocol plays a crucial role in implementing Industry 4.0 in the manufacturing industry. It is an industrial communication standard that ensures the interoperability of devices and systems used in the factory.
It utilizes standardized protocols for data exchange between various devices and systems, regardless of the manufacturer or technology used. Consequently, different systems in the factory communicate seamlessly, resulting in improved efficiency, reduced downtime, and fewer errors.
Moreover, this protocol enables real-time data collection and analysis from the production process, a pivotal aspect of Industry 4.0. This leads to better insights into factory performance and aids in making data-driven decisions.
Who uses it?
It is used by various companies and organizations in the industry, including manufacturers, system integrators, and software vendors. This protocol is particularly popular in the manufacturing industry, where it is used to integrate and communicate between various systems and devices in the factory. OPC is also widely used in the process industry, where it facilitates data exchange between control systems, sensors, and actuators.
OPC and SCADA
These are two technologies that are often used together in the industry. OPC is used to exchange data between different systems and devices, while SCADA is used to collect, monitor, and control data in a production environment.
SCADA systems provide a visual interface through which operators can monitor and control the performance of the factory. This often includes monitoring production lines, machinery, and equipment and collecting data such as temperature, pressure, flow, and level. Using this protocol, this data is collected and transmitted in real-time to the SCADA system, which then visualizes the data and enables operators to monitor and control the performance of the factory.
OPC and Ignition
Ignition is a software platform for managing industrial automation used for SCADA, HMI (Human Machine Interface), and MES (Manufacturing Execution System). It is designed to be flexible, scalable, and powerful, offering a wide range of features for automating industrial processes.
Ignition utilizes OPC technology to collect and integrate data from various devices and systems in the factory. Using Unified Architecture, Ignition exchanges data with other systems and devices in the factory.
Ignition also provides data processing features that enable businesses to perform real-time analysis and optimize factory performance. It is also easy to integrate with other systems, such as ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning), making it an end-to-end solution for industrial process automation.
Advantages of Ignition compared to other systems:
- Flexibility and scalability: Ignition is designed to be flexible and scalable, easily customizable to the needs of a specific production environment. It is easy to customize and expand with new features and modules without the need for expensive upgrades or software modifications.
- Cost savings: Ignition is based on a subscription model, meaning businesses only pay for the features and modules they need. This leads to significant cost savings compared to traditional SCADA systems.
- Faster development and implementation: Ignition has an intuitive and user-friendly interface that makes it easy to develop and deploy applications. This results in shorter development and implementation times, helping businesses start up their production processes faster.
- Wide compatibility: Ignition supports a wide range of hardware and software protocols. This means Ignition is able to exchange data with a wide range of devices and systems in the factory.
Discover Ignition
your way
Start building
For developers
Get started with your own Ignition applications right away.
- Download and install Ignition easily and quickly.
- Explore all features.
- Connect unlimited tags, PLCs, databases, and devices.
Discover how Ignition solves your technical challenges without limitations.
See Ignition in action
For managers
Explore Ignition without any technical knowledge in the demo environment.
- No installation required.
- See how Ignition automates and visualizes processes.
- Adjust live values and see instant results.
Experience real-time automation and discover what it can offer your business.
Want to really know what Ignition can do for you?
Let us come to you for a free demo.
- Meet with our experts and ask all your questions.
- Get personalized advice.
- See how Ignition can optimize your processes.
The perfect opportunity to collaborate with specialists and see exactly how Ignition can help you achieve your business goals.
